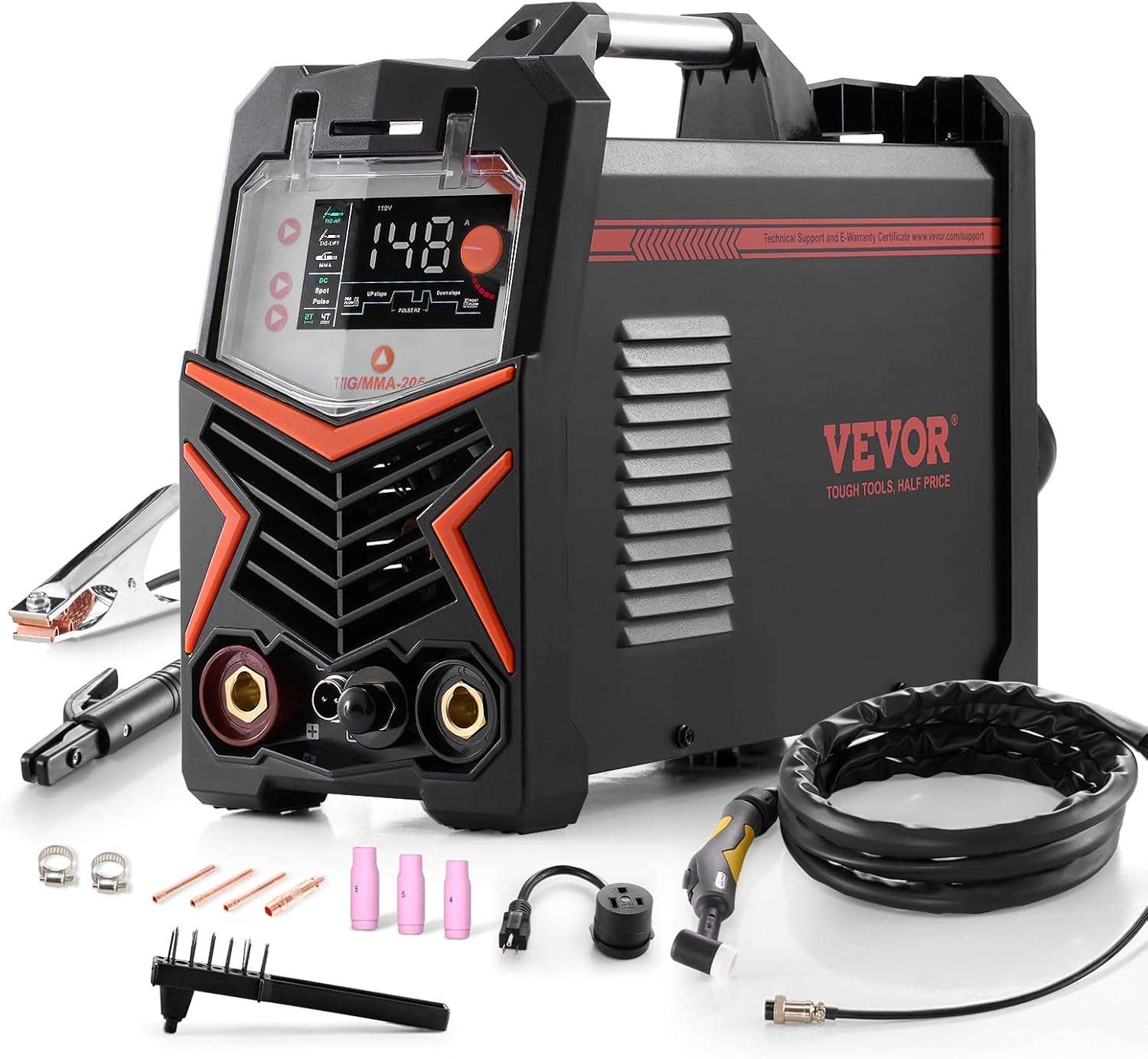
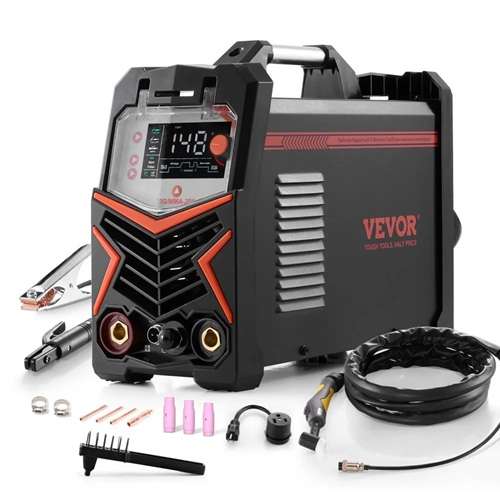
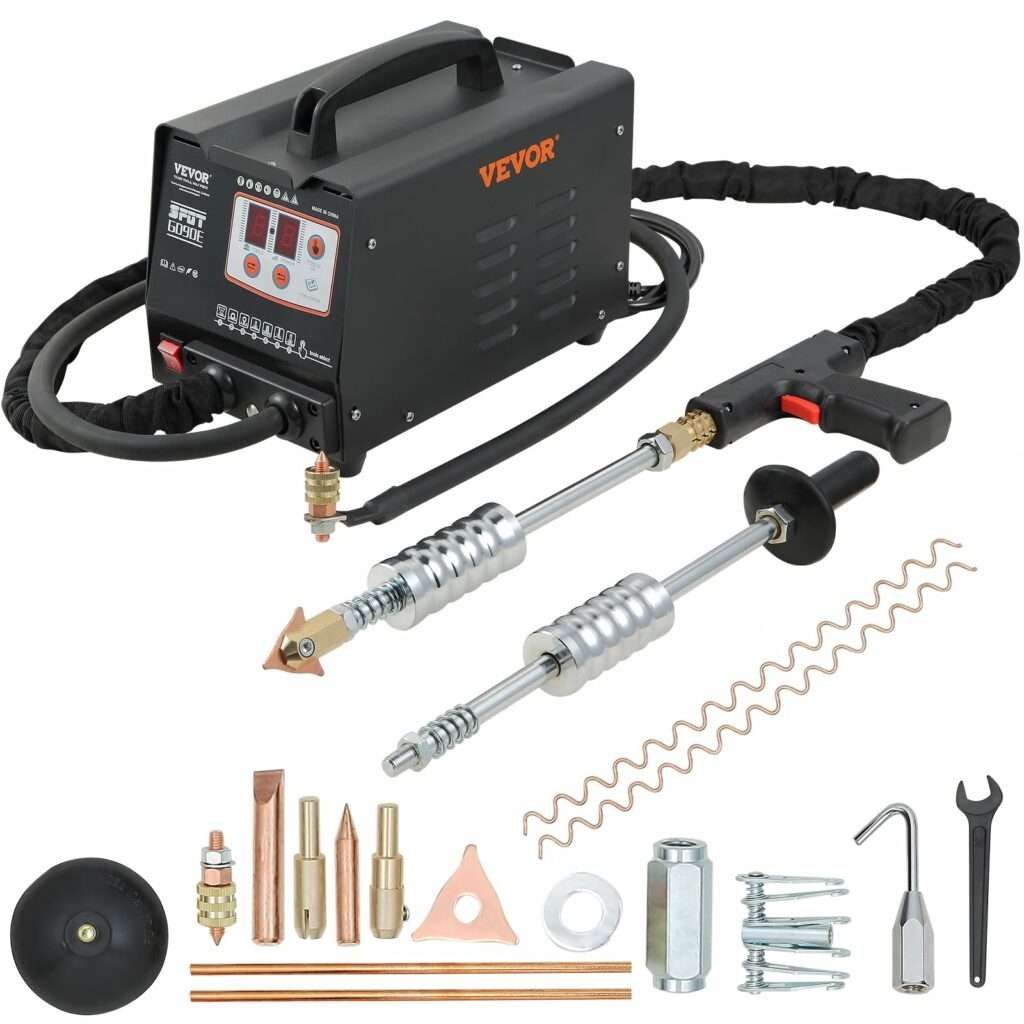
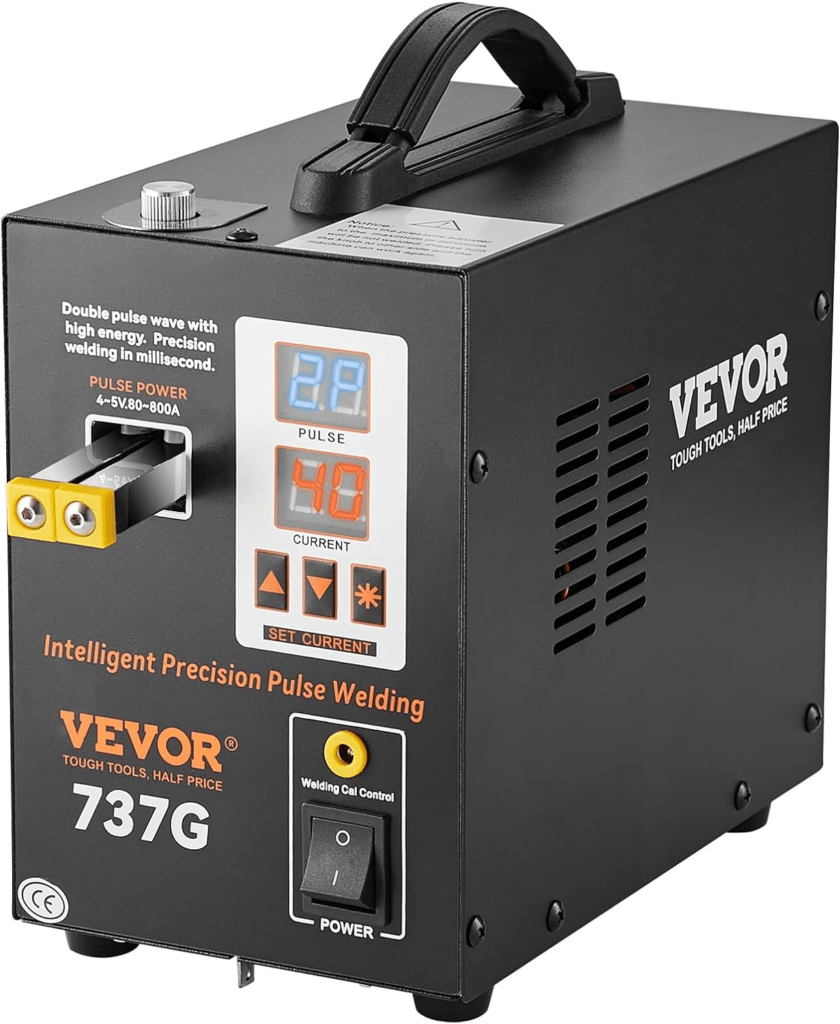
TIG welding (Tungsten Inert Gas welding) is one of the most precise and high-quality welding processes used today in industry, craftsmanship and advanced metal fabrication. Thanks to exceptional control of the weld pool, TIG welding produces clean, strong and visually flawless welds with outstanding consistency.
TIG, MIG MAG, MMA, SPOT WELDING AND STUD WELDING FOR DENT REPAIR
Trusted and verified affiliates links
On this page dedicated to TIG welding, you will find a complete guide to understanding, mastering and improving this demanding welding process. From choosing the right TIG welding machine to fine-tuning settings and applying professional welding techniques, this resource provides reliable and practical information for achieving high-quality TIG welds.
1. Introduction to TIG Welding (Tungsten Inert Gas)
TIG welding is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode combined with an inert shielding gas, usually argon. This method allows for extremely precise welds without spatter, offering excellent penetration control and a smooth, high-quality weld bead.
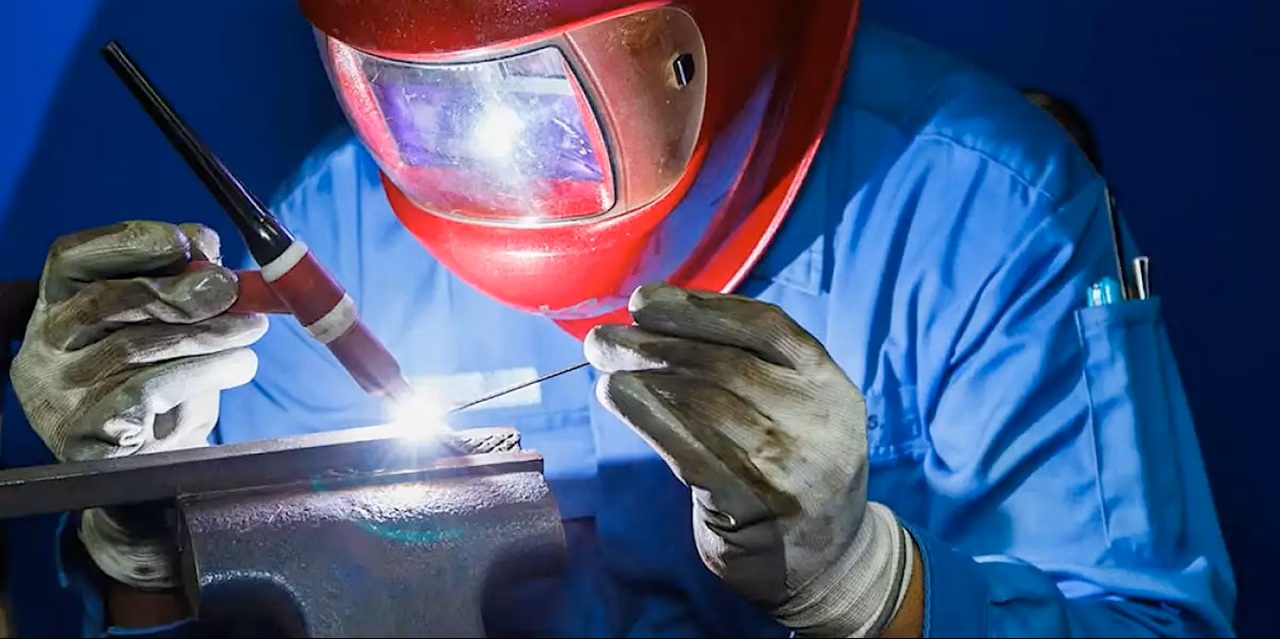

TIG welding is particularly valued for applications requiring a perfect finish, such as pressure vessel fabrication, pipe welding, aerospace manufacturing, the food industry and high-end structural metalwork.
2. Key Advantages of TIG Welding
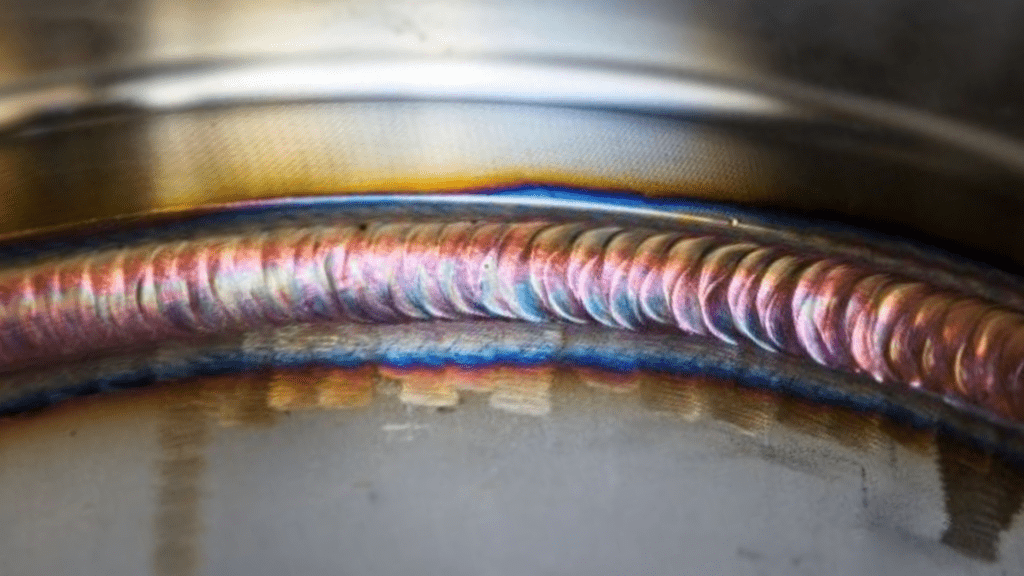
TIG welding offers numerous technical advantages. It provides outstanding control of the weld pool, exceptionally clean welds and excellent mechanical strength. Compared to other welding processes, thermal distortion is significantly reduced.
High quality and precision in TIG welding
By using a tungsten electrode and a separately fed filler metal, TIG welders can precisely control the amount of molten metal. This level of accuracy makes TIG welding ideal for thin materials, complex components and visible weld joints.
Versatility of weldable materials
TIG welding is suitable for a wide range of materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminium, copper, titanium and various alloys. With an AC/DC TIG welding machine, both aluminium and stainless steel can be welded efficiently using a single setup.
3. How a TIG Welding Machine Works
The TIG welding process is based on generating an electric arc between a tungsten electrode and the workpiece. Argon shielding gas protects the weld pool from oxidation, ensuring a clean, strong and durable weld.
Key components of a TIG welding setup
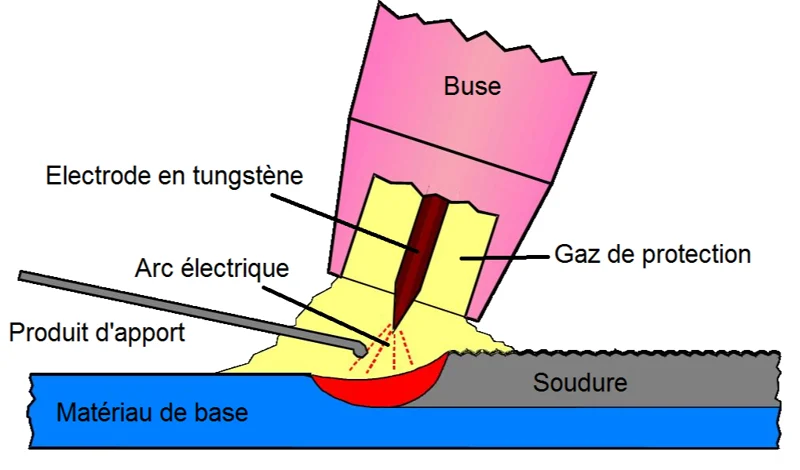
A TIG welding machine typically consists of a power source, a TIG torch, a tungsten electrode, shielding gas and, when required, a filler metal. Each component plays a critical role in achieving consistent and high-quality TIG welds.
4. Essential Settings for Successful TIG Welding
Proper settings are crucial in TIG welding. Welding current, current type (AC or DC), shielding gas flow rate and electrode diameter directly influence weld quality and overall performance.
Adjusting the welding current
The welding current must be adapted to the material thickness and type. Excessive current causes overheating, while insufficient current results in poor penetration and weak welds.
Setting the shielding gas flow rate
The shielding gas flow rate is a key factor in TIG welding, as it protects both the weld pool and the tungsten electrode from oxidation. Incorrect gas flow can compromise weld quality even when electrical parameters are properly set.
Recommended TIG gas flow rates
- Thin sheet metal (1–2 mm): 6–8 L/min
- Medium thickness (3–5 mm): 8–10 L/min
- Thick materials: 10–12 L/min
- Outdoor welding / drafts: 12–15 L/min
Factors affecting gas flow rate
- Nozzle diameter: Small nozzle → lower flow rate, large nozzle → higher required flow
- Electrode stick-out: Short stick-out → more stable shielding, long stick-out → slightly higher flow
- Welding position: Flat → standard flow, angled or vertical → slightly increased flow
- Environment: Enclosed workshop → normal flow, drafts → increase flow or shield the area
5. Professional Applications of TIG Welding
TIG welding is widely used in industries where weld quality is critical. Common applications include aerospace manufacturing, pharmaceutical production, stainless steel piping, precision mechanical components and the restoration of high-value metal parts.
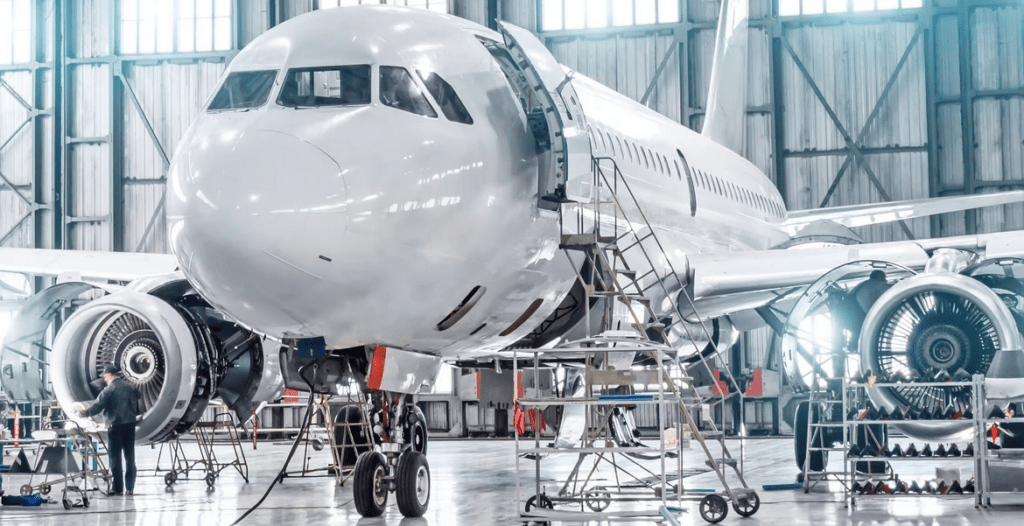

6. Safety and Best Practices in TIG Welding
TIG welding requires strict adherence to safety regulations. Personal protective equipment is essential, including a welding helmet, insulated gloves, flame-resistant clothing and respiratory protection when necessary.
Training and expertise of the TIG welder
A skilled TIG welder stands out through precise hand control, in-depth material knowledge and the ability to fine-tune welding parameters. Continuous training is a key factor in achieving both performance and safety.
Conclusion: Why Choose TIG Welding?
TIG welding is the preferred solution for applications requiring precision, reliability and a superior visual finish. When properly mastered, it enables durable, high-performance welds that meet the demands of the most technically advanced industries.
rer Modification de code Sortir de l’éditeur de code Lien sites Écrivez du texte ou du HTML